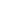
manufacturing process
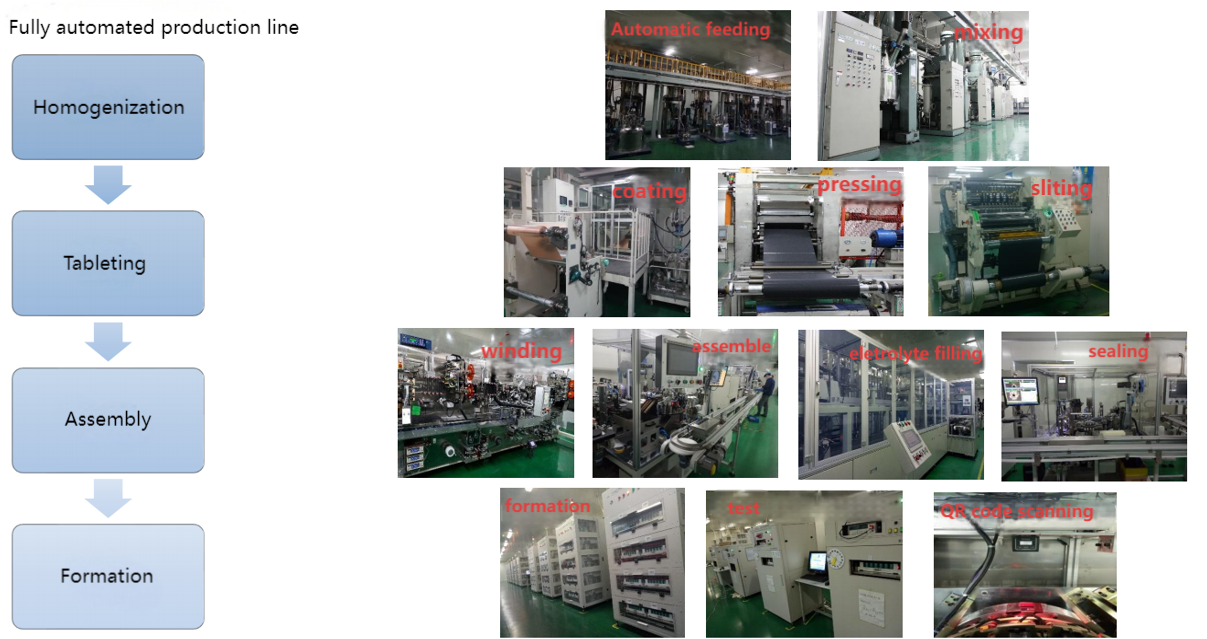

The lithium battery manufacturing process primarily consists of three stages: front-end electrode sheet production, mid-stage cell assembly, and back-end testing and packaging. This involves over 20 key processes, including mixing, coating, rolling, slitting, winding, liquid injection, and formation.
Front-end Process: Electrode Sheet Production
Mixing: The positive electrode material (such as LiCoO₂, LiFePO₄) or negative electrode material (graphite) is mixed with a conductive agent and a binder and stirred under vacuum to form a slurry. The solvent for positive electrode slurry is typically NMP, while deionized water is used for negative electrode slurry.
Coating: The slurry is evenly applied to metal foil (aluminum foil for the positive electrode/copper foil for the negative electrode) and dried to form the electrode sheet. The coating thickness accuracy must be controlled within ±2μm, directly impacting battery capacity and safety.
Roller Pressing: High-pressure compaction of the electrode sheets increases energy density. The positive electrode achieves a compaction density of approximately 3.4-3.8 g/cm³, while the negative electrode achieves approximately 1.5-1.7 g/cm³.
Slitting and Die-Cutting: The electrode sheets are cut to the desired size, ensuring burr-free edges to prevent short circuits.
Mid-Stage Process: Cell Assembly
Winding/Lamination: The positive and negative electrode sheets and separators are wound together to form cells (cylindrical/prismatic cells) or stacked (pouch cells).
Assembly and Filling: After the cell is placed in the casing, the electrolyte is injected, requiring precise control of the injection volume.
Packaging: The cell is sealed using laser welding or mechanical pressing to ensure an airtight seal.
Post-Stage Process: Activation and Testing
Formation: The cell is activated during the initial charge to form the SEI (solid electrolyte interface) film. The current is typically 0.02C-0.1C.
Capacity Sorting: Charge and discharge tests are performed to screen for capacity consistency. The voltage accuracy of the capacity sorting cabinet must reach ±1mV.
Aging and Sorting: After room temperature storage, parameters such as voltage and internal resistance are tested and then graded and packaged.